How To Propagate Indoor Plants
What is propagation?
Propagation of plants involves producing new plants from parent plants. There are several methods for plant propagation, which are discussed here.
Vegetative propagation
The most common way to reproduce Indoor Plants is through vegetative propagation. You can propagate houseplants using the following parts of the plant:
Stem,
Root,
Node,
Leaf.
Conditions for propagation
- Choose healthy plants. It should not have any infection.
- Use sterilized media.
- Sharp tools
- High heat,
- Light that’s too bright, etc.
- Timing for optimum results
In most cases, vegetative propagation results in a new plant quickly; however, some plants may not respond well to this method. To increase the chances of successful propagation,
Environmental Conditions
- Ensure the light is bright. Avoid placing the growing plants in dark areas.
- Keep the soil moist, but not waterlogged.
- Since houseplants are typically tropical, they thrive in humid conditions. To maintain moisture, mist the upper parts of the plants to prevent drying out. However, be cautious, as excessive humidity can lead to infections.
- The ideal temperature for young indoor plants is room temperature or slightly above, around 25-30°C (75-85°F).
Propagation Media
Common media used for propagating indoor plants typically include garden soil, cocopeat, and compost in a 1:1:1 ratio. Here are some other media and their purposes:
- Sand: Provides good drainage and aeration, maintains a pH of 6.5, and allows easy root penetration.
- Water: Some plants, like pothos (money plant), are propagated in water. Once roots develop, they can be transferred to solid media.
- Cocopeat: Used either alone or in combination, cocopeat provides organic material to the newly growing plant, makes the media soft, and helps retain moisture.Vermiculite and Perlite: These large mineral particles aid in water drainage, improve aeration, and keep the soil pH neutral. They are often used in combination or as a top layer on planters to give them a unique appearance.

- Bark: provides very good water drainage and aeration, acidic pH

- Compost: Compost is the decay of plants and animals. There are many types of compost.It helps in keeping the growing media soft and can hold the water in the soil.
Compost and garden soil should not be used alone and must be mixed in proportion because they can be too dense for soft, growing roots, increasing the risk of infection.
Vegetative Propagation Methods
Method of propagation:
There are many methods for indoor plant propagation. The method of propagation depends upon the type of plant. These methods are
- Cutting.
- Rooting a leaf
- Rooting
- drafting
- Dividing,
1-Cuttings
Cuttings can be made using a leaf or stem.
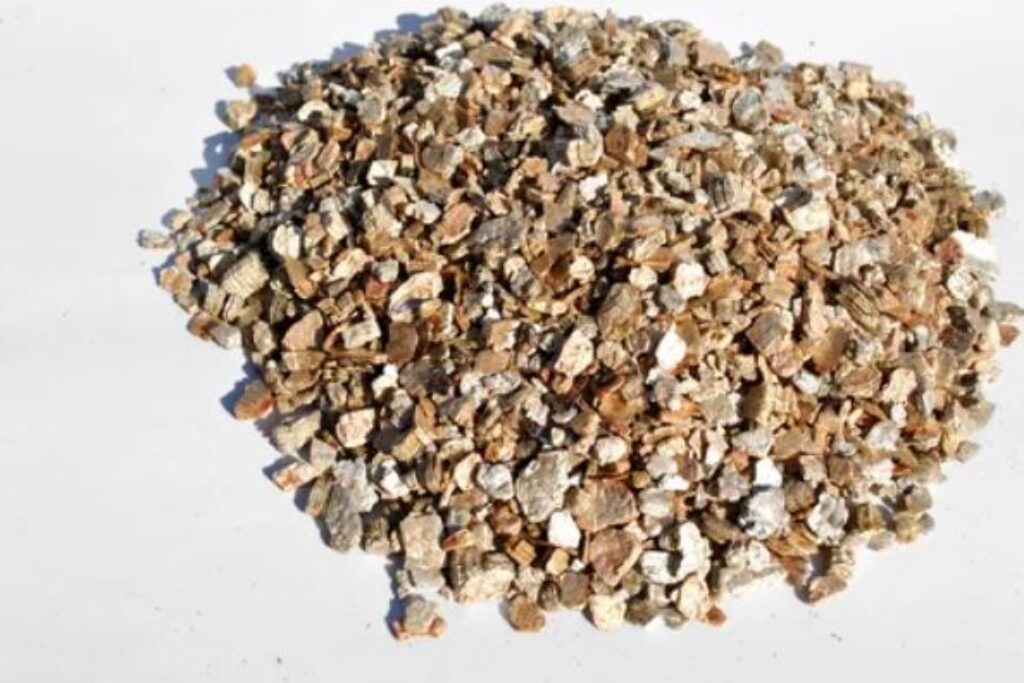
Leaf cuttings

- Take cuttings from healthy leaves:
- Cut a piece that is 3 to 6 inches long with at least two nodes.
- Remove the lower part of the cutting.
- Leave at least half an inch of the petiole to support the leaf.
- Allow the cuttings to dry for 48 hours to let the cut edges harden.
- Dip the leaf end in a rooting hormone. Lightly tap to remove any excess hormone.
Auxin is used as a rooting hormone and is available in powder, gel, or liquid form. However, only a small amount is needed, as excessive use can damage the plant. To apply the hormone, dip the leaf in it and gently tap off any excess. Then, place the cutting in a warm location with high humidity and bright, indirect light.
Plants that propagate with leave cuttings are
- Snake plant
- Jade Plants
- ZZ plants
- Pepermonia
- African violet
- Rex begonias
Stem cuttings:
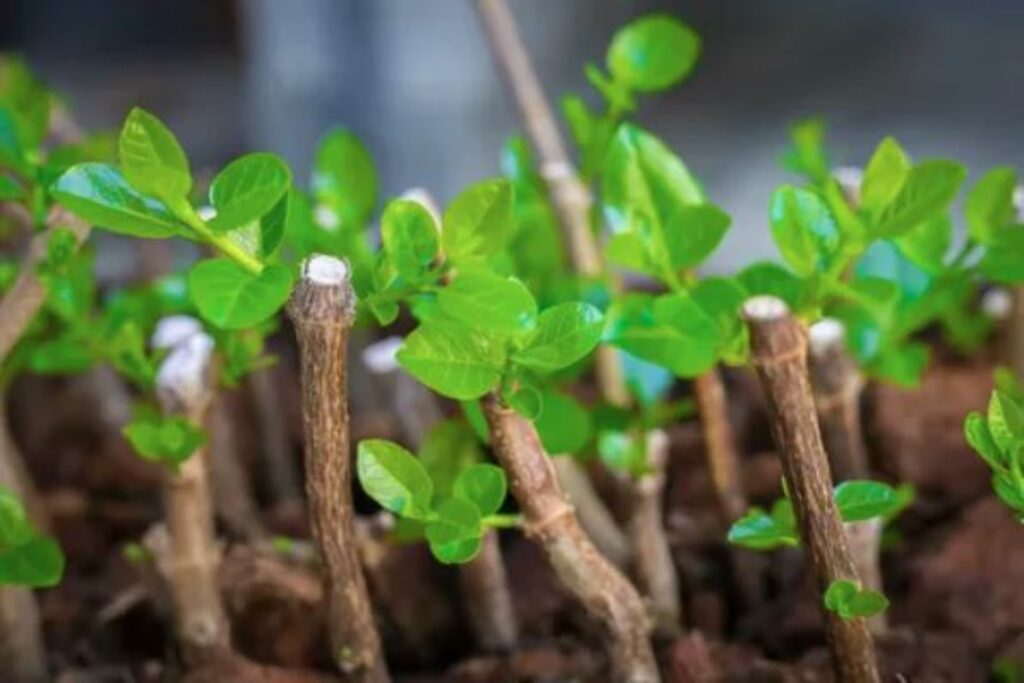

- Select a 2- to 10-inch portion of the stem with at least two nodes and cut it.
- You can treat the stem cutting in one of two ways:
- Remove the lower leaves from the cutting, then stick the stem vertically into the rooting media with at least one node buried in the media.
- Alternatively, lay the stem horizontally on the media, with half of the stem inserted into it.
- Water the cutting regularly.
- After a few days, roots will develop from the nodes that are buried in the soil, and shoots will emerge from the nodes that are above the soil.
- Once the stem has developed roots, transplant the plant into soil.
Plants suitable for stem cuttings are
- Devil’s Ivy, Pothos,
- Monstera , Swiss Cheese Plant)
- Heartleaf Philodendron Chinese Money Plant
- Schefflera arboricola (Dwarf Schefflera
- Holiday Cactus
- Tradescantia,inch plant
2. Rooting from a leaf
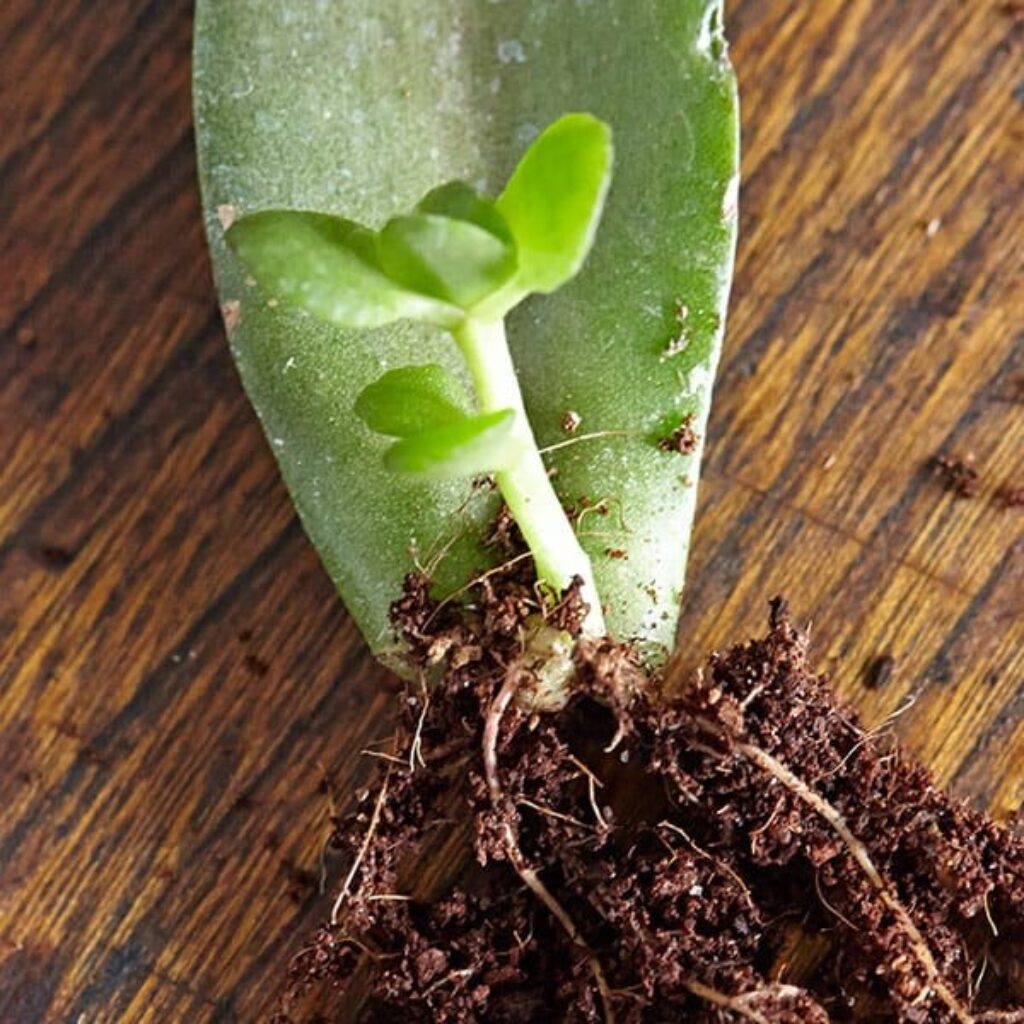

This method can be tricky and may require some trial and error, as not every leaf will successfully root. Succulents and jade plants are commonly propagated through leaf rooting.
Steps to rooting a leaf:
- Cut the leaf from the plant as cleanly as possible.
- Allow the leaf to dry out for a couple of days to let the cut end scab over.
- Dip the tip of the leaf in rooting hormone, then insert at least two-thirds of the leaf into fresh potting soil, ensuring the leaf is positioned so it will grow in the right direction.
- Gently press the potting mix around the leaf.
- Propagation involves taking a part of a mature plant and growing it into a new, independent plant.
From Leaf whole leafe
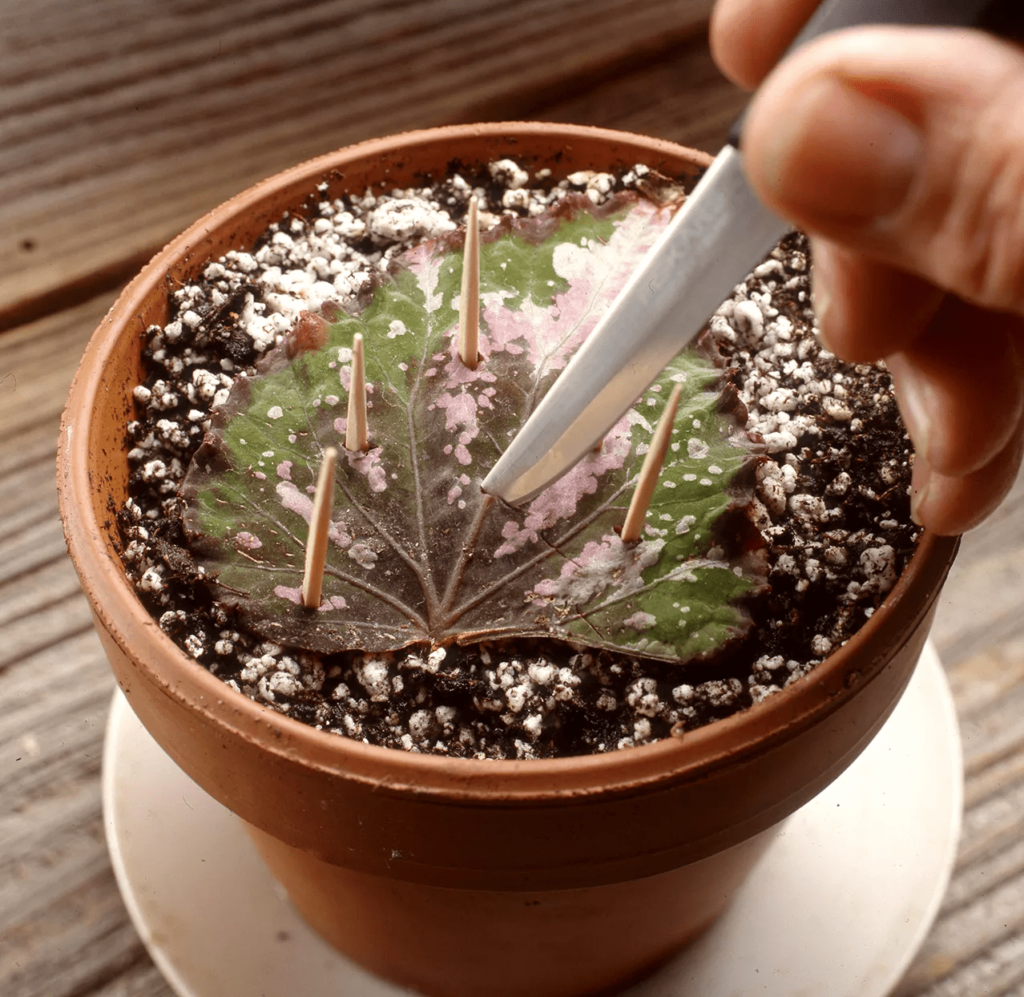

- Put the whole healthy leave on pot soil.
- Fix it with tooth pics
- Cut the leave with sharp knife in the way that each part will have petiol of the leave.
- Keep it moist and cover it with plastic bag
- Root wil apear from each cut and after some time small leaves will grow form these leaves.
Rex begonia, is propagted in this way.
3-Grafting
Grafting is used when you want to propagate a plant with specific traits, such as desired fruit or flower characteristics, or to promote rapid growth. In this method, a section of one plant is placed onto the rootstock of another plant.
Grafting is applied
- When a plant has a slower growth rate, such as succulents.
- For plants that lack chlorophyll and cannot photosynthesize efficiently.
- When plants require more nutrients than their own root system can provide.
The most common grafting methods are
1-flat/side graft
2-apical-wedge graft.
Flat or side graft:
This process involves:
- Select a plant with the desired characteristics (scion) and another plant for the rootstock.
- Cut both plants at an angle using a sharp knife. The scion should be cut from the lower side, and the rootstock should be cut so that only the root with some stem remains.
- Ensure the two pieces fit together properly. Sharpen the angle if needed.
- Align the plant sections so their conducting tissues match, then join the two pieces and twist them slightly to remove any air bubbles.
- Secure the grafted sections with an elastic band to hold them in place.
Apical-wedge graft:
- Plants that do not respond well to flat grafting can be propagated through apical wedge grafting, which is commonly used for cacti.
- Start by selecting a plant to serve as the rootstock.
- Slice the rootstock vertically down the center through the conducting tissue.
- Insert the scion (the plant with the desired characteristics) into this “slit.”
- Cut a piece of the scion approximately 2 to 3 inches long.
- Pare both sides of the scion to expose the conducting tissue, then insert it into the rootstock, aligning the conducting tissues.
- · Cover the graft with grafting tape or an elastic band to secure it.

4-Division
(How to propagate offsets/How to seprate the baby plant)
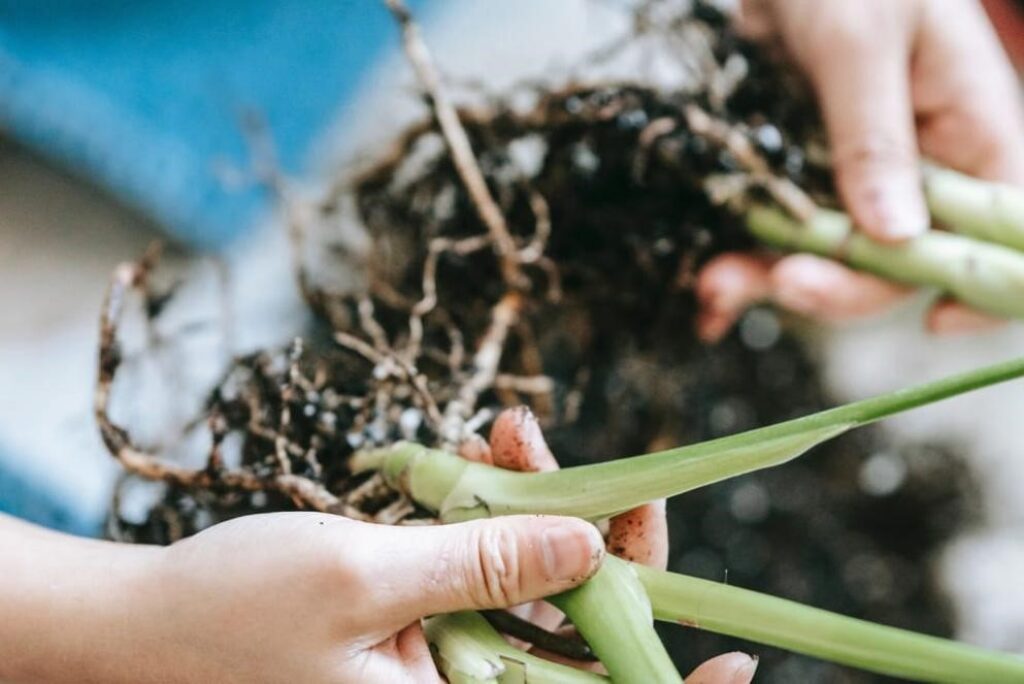

This metod is used in plants those grow in clumps like snake plan. Gently pull or cut apart the plantlets.
The best time to divide indoor plants is in spring, as it is their growing season. This method is one of the easiest ways to propagate houseplants. If you’re a beginner, start with plants that grow in clumps, as they are easier to divide.
- Zz plants
- ferns
- Monstera or Swiss cheese plant
- African mask or elephant’s ear
- Asparagus fern
- Coffee plant
- aralia (Plerandra elegantissima, syn. Dizygotheca elegantissima)
- Japanese aralia
- Money tree (Pachira aquatica)
Steps to dividing indoor/houseplants:
- Remove the plant from the pot and examine the root ball. Choose a healthy area to divide.
- Use a sharp knife to cut the plant into sections, ensuring you don’t damage the roots. If the plants are soft, gently separate them with minimal force.
- If the “baby plants” have roots, cut them from the mother plant and pot them in soil.
- If they don’t have roots, place them in pots filled with compost and water them. Roots will develop over time. Once they have rooted, you can separate them from the mother plant.
- Transfer the divided sections into the appropriate media. Firmly press the roots into the soil.
- Keep the plants in warm, humid conditions and water them regularly.
- After a few days, the plants should begin to grow.